Stages of Cannabis Plant Growth: A Journey from Seed to Harvest

Cannabis plant growth, encompassing its cultivation and development, represents a journey with deep historical roots and a wide range of applications. Originating in the ancient fields of Asia and evolving into today’s advanced high-tech greenhouses, cannabis has been an integral part of human agriculture for centuries. For both commercial growers and enthusiasts, a thorough understanding of the various stages of cannabis plant growth is essential.
This article explore the life cycle of the cannabis plant, detailing the transformation from a mere seed to a fully mature plant, and highlighting the complexities and nuances of its growth process.
Germination
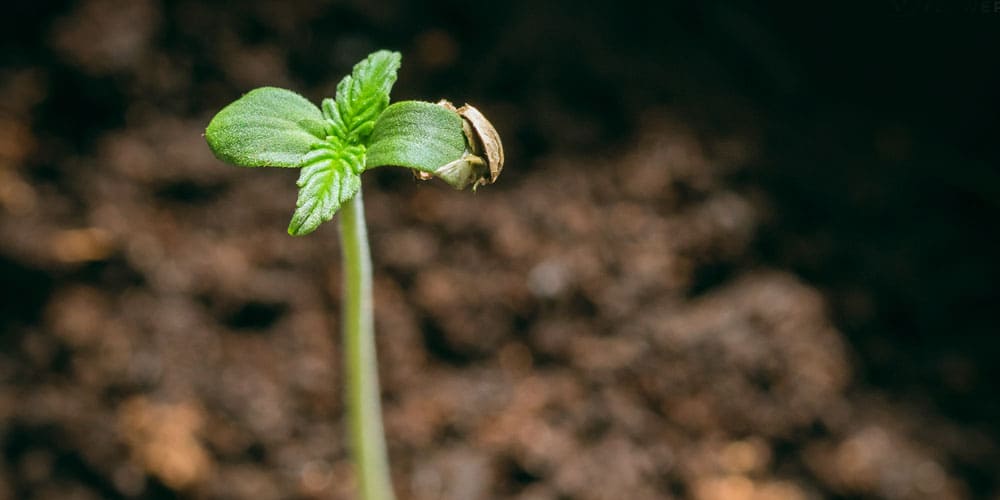

The journey of a cannabis plant commences with the germination stage, a critical and foundational period where the dormant seed springs to life. Germination is initiated when the seed is exposed to essential conditions like moisture, warmth, and darkness, typically occurring within 24 to 72 hours. During this phase, the hard outer shell of the seed cracks open, allowing a small, delicate taproot to emerge. This taproot serves as the primary anchor of the plant, securing it in its growing medium.
Concurrently, the emergence of the seed’s first leaves, known as cotyledons, marks the beginning of the photosynthetic process, crucial for the plant’s growth and energy production. The success of germination is heavily influenced by several factors, including the quality and genetic makeup of the seed, the environmental conditions provided, and the grower’s technique and experience. Germination is a sensitive stage in the plant’s life cycle, demanding meticulous attention to moisture levels, temperature, and overall care.
To increase the likelihood of successful germination, growers often resort to various methods. One popular method is the paper towel technique, which involves placing seeds between moist paper towels to encourage sprouting. Alternatively, some growers prefer direct planting into a suitable growing medium, providing an undisturbed environment for the seed to begin its development.
Dive into the exclusive realm of BOSS OG Sauce Cartridge, featuring 1000 milligrams of resin from the balanced Boss OG strain. This 50% indica/50% sativa hybrid offers a journey of cerebral uplift and deep relaxation.
Seedling Stage
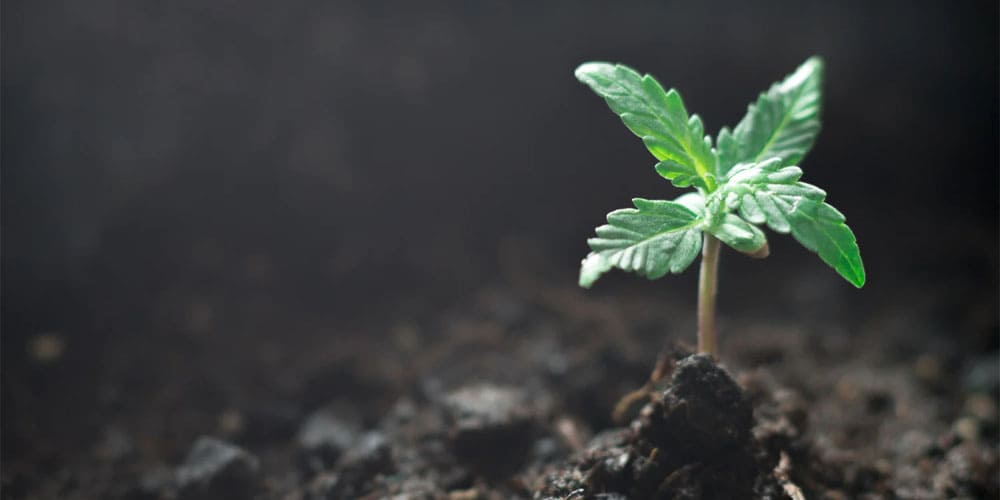

After germination, the cannabis plant progresses into the seedling stage, a period that typically spans 2-3 weeks and is crucial for laying a robust foundation for the plant’s subsequent growth. In this stage, the young cannabis plant, now equipped with its initial cotyledons and the first true set of leaves, is particularly vulnerable and sensitive to environmental factors. The seedling’s health during this phase sets the tone for its overall development and future productivity.
During the seedling stage, ensuring optimal conditions is paramount for the plant’s health and vitality. Proper lighting is critical, with the young cannabis plant needing about 18 hours of light and 6 hours of darkness each day to thrive. Additionally, maintaining the right levels of humidity and temperature is essential to support healthy growth. As the seedling matures, its root system starts to expand, and more leaves begin to develop, gradually forming the distinctive shape of the cannabis leaf.
Vegetative Stage

The vegetative stage of the cannabis plant is characterized by a period of significant and rapid growth, typically lasting between 3 to 16 weeks. This stage is crucial as the plant develops most of its foliage and branches during this time. For growers, particularly those cultivating cannabis indoors, there is considerable control over the duration of this stage. Extending the length of the vegetative stage allows the plant to grow larger, which can lead to increased yields when it finally comes to harvest.
In the vegetative phase, the cannabis plant demands a high amount of light, needing approximately 18-24 hours of light exposure each day. This extensive light exposure is pivotal in stimulating robust growth, resulting in a plant that is both bushier and taller. Along with light, the plant’s nutrient needs escalate, with nitrogen playing a vital role in the development of healthy leaves and stems. Adequate nitrogen ensures vigorous vegetative growth, setting the stage for a fruitful flowering phase.
During this vegetative period, growers often implement various plant training techniques to optimize the plant’s exposure to light and improve air circulation around the foliage. Techniques such as topping, where the main stem is cut to encourage the growth of multiple stems, or low-stress training (LST), which involves gently bending and tying down branches to encourage horizontal growth, are popular. These methods are designed to create a more evenly distributed canopy, allowing light to reach lower parts of the plant, thus maximizing the overall growth potential and increasing the eventual yield.
Unleash the power of the Kool Aid Double Blunt. This potent hybrid boasts a high THC level and a delightful sweet, fruity aroma. Paired with APE’s signature double blunt, it’s an irresistible force for any cannabis enthusiast.
Pre-flowering Stage

The transition from the vegetative stage to the flowering stage in cannabis cultivation is marked by an intermediate phase known as the pre-flowering stage. This stage typically lasts between 1 to 2 weeks and is a critical period where the plant begins to respond to the changing light conditions. In outdoor cultivation, the onset of pre-flowering is naturally triggered by the shorter days as summer transitions into autumn. This change in light duration signals to the plant that it is time to start preparing for the reproductive phase of its life cycle.
During the pre-flowering stage, one of the most crucial tasks for growers is identifying the sex of their cannabis plants. This is the time when the sexual characteristics of the plants become distinguishable. Female plants start to develop pistils, which are small, white, hair-like structures. These pistils are the precursors to the buds that will later be harvested. In contrast, male plants begin to produce small pollen sacs. Identifying and removing male plants is a common practice in cannabis cultivation, as it prevents the pollination of female plants.
Pollination can significantly impact the quality and quantity of the female plant’s buds by diverting energy to seed production rather than bud development, which is generally undesirable in cannabis cultivation.
Flowering Stage

The flowering stage represents the culmination of the cannabis plant’s life cycle and is the most critical phase for bud production. Typically extending for about 6 to 8 weeks, this stage is triggered when the plant experiences a shift in its light exposure to 12 hours of light and 12 hours of darkness each day. This specific light cycle is designed to replicate the natural decrease in daylight hours that occurs in the outdoor environment, signaling to the cannabis plant that it’s time to enter its reproductive phase and begin flowering.
In the initial weeks of the flowering stage, cannabis plants often experience a rapid and significant growth spurt, commonly referred to as the “stretch.” During this phase, plants can double or even triple in height, rapidly expanding in size. Concurrently, the formation of buds starts at the nodes, which are the points where the leaves and branches intersect. This stage also brings a change in the plant’s nutritional requirements, with an increased need for phosphorus and potassium to adequately support the development and maturation of the buds.
Throughout the flowering stage, close and careful monitoring of environmental conditions becomes increasingly important. Maintaining optimal levels of humidity and temperature is crucial, as the plant’s dense foliage and budding sites are particularly susceptible to issues like mold and pest infestations. As the flowering stage progresses, the trichomes – the tiny, crystal-like structures that appear on the surface of the buds – begin to change in color. This change in trichome color is a key indicator used by growers to determine the optimal time for harvesting.
Explore relief with Hippie Crasher Sauce Cartridge, an indica strain tailored for pain management, nausea control, and neuropathic issues. It’s the ideal solution for those facing tough days while managing debilitating conditions, helping you push through with ease.
Harvest

Determining the optimal time to harvest cannabis is a critical factor in maximizing the plant’s potency and flavor, a decision that requires careful observation and timing. Growers pay close attention to several key indicators to assess the plant’s readiness for harvest. One of the primary signs is the darkening and curling of the pistils, the tiny hair-like structures on the buds. Additionally, the color of the trichomes, the microscopic resin glands on the buds, is a crucial indicator. Clear trichomes typically suggest that the plant is still under-ripe, while milky or cloudy trichomes indicate peak THC levels and maximum potency.
The actual process of harvesting involves several steps to ensure the quality of the final product. The first step is cutting down the plant, followed by meticulously trimming the buds to remove excess leaves. After trimming, the buds must undergo a curing process, which is essentially a controlled drying phase. Proper curing is vital as it greatly enhances the flavor, aroma, and overall quality of the cannabis. During curing, the moisture from the buds evaporates slowly, allowing for the development of richer flavors and a smoother smoking experience.