What is Industrial Hemp?

Industrial hemp, in the rapidly changing world of agriculture and sustainable resources, has gained increasing recognition for its versatility and environmental benefits. Despite a complicated history and often being misunderstood, industrial hemp is making a strong comeback as a valuable resource across multiple industries. This comprehensive exploration examines industrial hemp, delving into its historical background, diverse applications, and the array of challenges and opportunities it presents in the modern era.
- Ditch Weed vs. Cultivated Cannabis
- Parts of the cannabis plant
- Marijuana, Cannabis and Weed: What is the Difference?
The Identity of Industrial Hemp

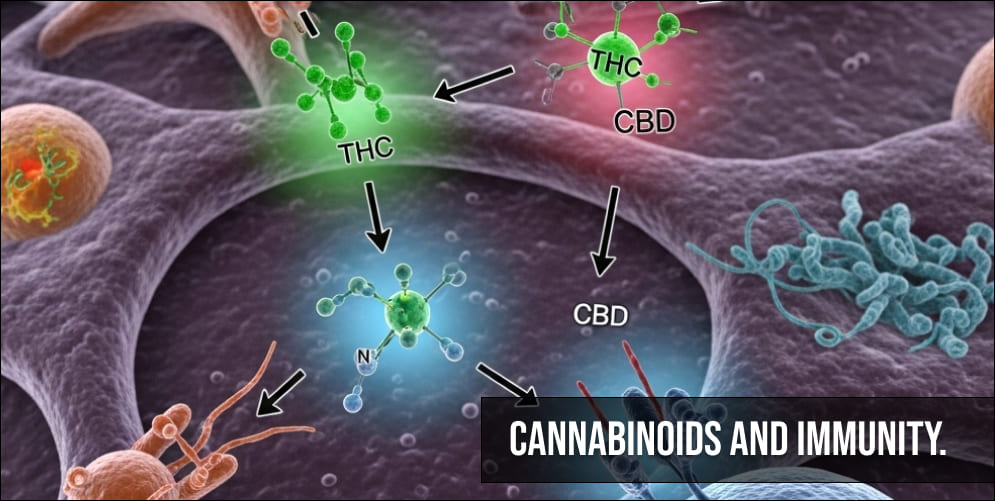
Industrial hemp, classified scientifically as Cannabis sativa L., is indeed a variety of the Cannabis plant, yet it is distinctly different from its more notorious relative, marijuana. The most significant difference between the two lies in their chemical makeup. Industrial hemp is characterized by its minimal THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) content, which is less than 0.3%. THC is the psychoactive compound found in higher concentrations in marijuana, responsible for its intoxicating effects.
Due to its low THC levels, industrial hemp does not produce the intoxicating effects typically associated with marijuana. This distinction makes it a safe and legally accepted agricultural product in numerous regions around the world. The cultivation and use of industrial hemp have gained popularity due to its versatility and the growing recognition of its potential in various industries, from textiles to biodegradable plastics, without the legal and psychoactive complications of marijuana.
Savor the exquisite depth of our Blackberry 10 Cannabis-Infused Gummies, a collection of 10 delightful treats. Infused with the succulent essence of blackberries, these gummies are expertly crafted to arouse the senses, satisfy cravings, and foster relaxation.
Hemp Through the Ages

The journey of hemp through history is as diverse as its applications. Evidence suggests that humans have cultivated hemp for over 10,000 years, making it one of the oldest known agricultural crops. Ancient civilizations utilized hemp for a range of purposes, including making textiles, paper, and even food. Its durability and ease of cultivation made it a preferred choice.
However, the 20th century witnessed a decline in hemp’s popularity, largely due to the rise of synthetic materials and legal restrictions related to the Cannabis family. Notably, the Controlled Substances Act of 1970 in the United States did not differentiate between industrial hemp and marijuana, causing a substantial drop in hemp cultivation. This period marked a significant shift in global perception and usage of hemp.
In recent years, there’s been a revitalization in hemp cultivation, driven by technological advancements and increased focus on sustainability. Changes in legislation in various countries now recognize the distinction between industrial hemp and marijuana, easing previous restrictions. This legal evolution has enabled farmers, researchers, and entrepreneurs to explore and expand hemp’s potential.
Exploring the Versatility of Hemp

Industrial hemp is renowned for its versatility, with applications spanning across numerous industries including textiles, construction, health and nutrition, and even emerging sectors like bioplastics.
- Textiles and Clothing: Hemp fibers, renowned for their exceptional strength, durability, and natural resistance to mold and ultraviolet light, stand out as an ideal material for clothing and textiles. These fibers offer a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to synthetic materials, aligning with the growing demand for environmentally responsible fashion. Hemp fabrics are not only durable but also biodegradable, presenting a compelling option for those seeking to reduce their environmental footprint.
- Construction and Building Materials: Hempcrete, an innovative construction material made from a blend of hemp fibers, lime, and water, is gaining recognition in sustainable building practices. Its composition results in a lightweight yet durable insulating material, prized for its excellent thermal and acoustic properties. Ideal for environmentally conscious construction, hempcrete not only provides efficient insulation but also contributes to the reduction of carbon footprint in building projects.
- Paper and Sustainable Packaging: Hemp serves as a highly efficient and faster-growing alternative to traditional wood pulp in the production of paper, marking a significant shift in sustainable manufacturing practices. Its rapid growth cycle and high yield make it an ideal resource for papermaking, reducing the need for deforestation and environmental degradation. Moreover, the advent of hemp-based packaging solutions has further expanded its ecological contributions.
- Health, Nutrition, and Therapeutics: Rich in proteins, essential fatty acids, and minerals, hemp seeds are nutritional powerhouses. Hemp oil is used in dietary supplements and skincare products. The CBD market, derived from hemp, is expanding rapidly, with applications in pain relief, anxiety management, and various therapeutic areas.
- Bioplastics and Environmental Solutions: Hemp is increasingly recognized as a valuable raw material in the production of bioplastics, marking a significant advancement in sustainable materials technology. These hemp-based bioplastics offer a biodegradable alternative to traditional petroleum-based plastics, representing a major stride in reducing environmental impact. By breaking down more easily and reducing reliance on fossil fuels, hemp bioplastics are seen as a crucial development in the effort to address plastic pollution and environmental sustainability.
Experience the exquisite fusion of Cotton Candy & White Truffle Hash Hole Pre-Roll. This 2.5g hybrid marvel combines Cotton Candy’s dreamy euphoria with the deep calm of White Truffle, crafting a harmonious and fulfilling journey.
Challenges and Opportunities

Despite its potential, industrial hemp faces several challenges. Misconceptions and legal complexities surrounding the Cannabis plant continue to hinder widespread adoption. Additionally, the lack of established supply chains and processing facilities can be a barrier for farmers and producers.
However, the opportunities presented by hemp are vast. As the world moves towards more sustainable and eco-friendly practices, hemp stands out as a viable solution. Its low requirement for pesticides and herbicides, combined with its ability to grow in various climates, makes it an attractive crop for sustainable agriculture.
Future of Industrial Hemp

The future of industrial hemp is indeed bright, with its potential applications continually expanding through ongoing research and development. This versatile plant is at the forefront of numerous innovations across various sectors. The range of hemp-based products is broadening, encompassing everything from biofuels to 3D printing materials. These developments are not only technologically significant but also carry immense potential for environmental sustainability, showcasing hemp’s adaptability and utility in modern industries.
As the global recognition of hemp’s economic and environmental benefits increases, more countries are beginning to embrace its cultivation and use. This growing acceptance is paving the way for hemp to play a more prominent role in industries around the world. The diversity of its applications, coupled with its eco-friendly attributes, positions hemp as a key player in the push towards more sustainable industrial practices. This trend suggests a future where hemp’s influence extends far beyond its current scope, driving innovation and ecological responsibility on a global scale.
Discover the soothing allure of WATERMELON OG live resin sugar diamonds. Known as ‘Watermelon Kush’ in some circles, this indica strain is a mystery blend of two unknown parents, renowned for its deeply relaxing effects.