A guide to cannabis deficiencies

As a cannabis cultivator, it’s essential to understand the nutrient requirements of your plants and be able to identify and address common deficiencies. Throughout the vegetative and flowering stages, cannabis plants have specific nutrient needs, and deficiencies can arise if those needs are not met.
In this guide, we will explore the most common nutrient deficiencies during each stage and provide insights on how to recognize and remediate them. By familiarizing yourself with these deficiencies and implementing the right solutions, you’ll be well-equipped to nurture healthy and thriving cannabis plants.
Common Nutrient Deficiencies During The Vegetative Stage
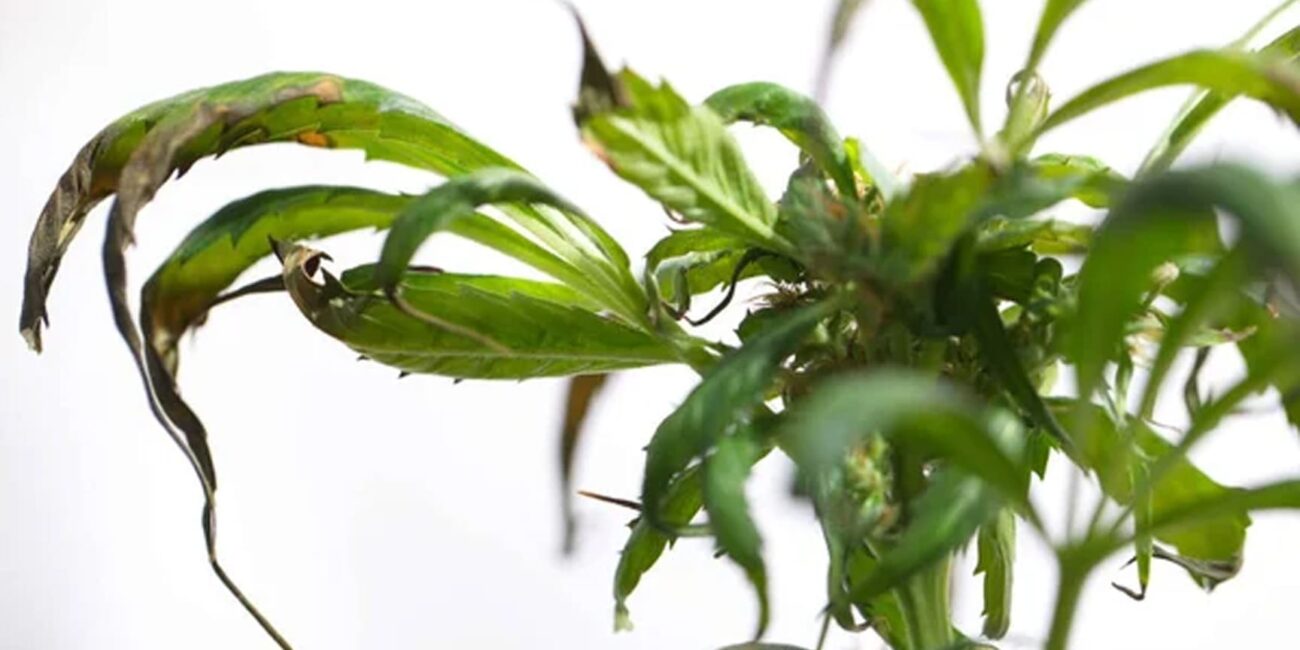

nitrogen deficiency
During the growth cycle of the cannabis plant, it requires varying levels of nutrients. One common deficiency that occurs more frequently during the vegetative phase is a lack of nitrogen.
Although the cannabis plant needs more nitrogen during the flowering phase, some growers mistakenly neglect to provide sufficient nitrogen during the vegetative phase. A nitrogen deficiency is characterized by progressive yellowing of the leaves, starting from the bottom and moving upward.
To address a nitrogen deficiency, there are several products available that can be added to water and fed to the cannabis plants. It’s crucial to exercise caution when applying nitrogen as too much can be detrimental to the plants.
It is advisable to start by adding additional nitrogen to the feeding schedule of one plant and observe its response before applying it to other plants.
magnesium deficiencies
On the other hand, magnesium deficiencies are more common during the flowering phase but can also occur during the vegetative phase.
A magnesium deficiency manifests as interveinal yellowing of the leaves, which is different from the overall yellowing observed in a nitrogen deficiency.
To remedy a magnesium deficiency, including more epsom salt in the feeding schedule is an effective approach. Epsom salt not only provides magnesium but also contains sulfur, which helps combat sulfur deficiencies.
Sulfur deficiencies
Sulfur deficiencies can arise during both the vegetative and flowering phases, and it can be challenging to distinguish them from magnesium or nitrogen deficiencies.
Common Nutrient Deficiencies During The Flowering Stage
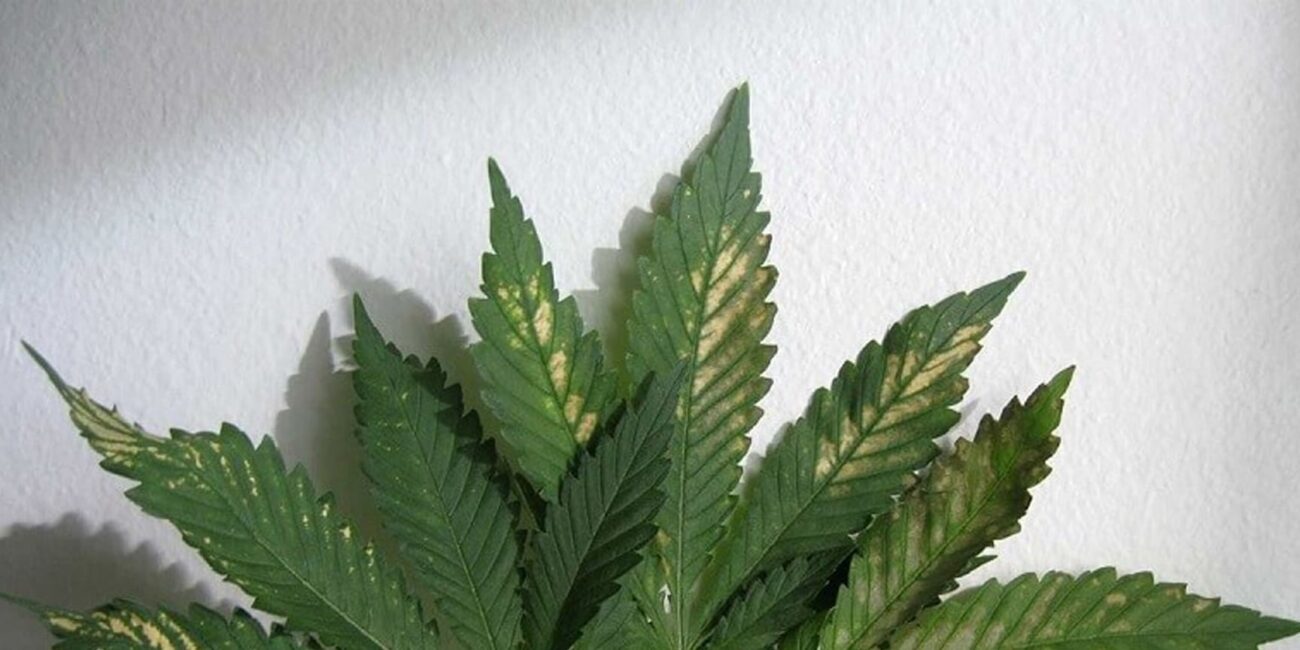

During the flowering stage of the cannabis plant, it has an increased demand for nutrients, leading to a higher likelihood of various nutrient deficiencies. In addition to the previously mentioned deficiencies, several others commonly occur during this phase of the plant’s growth cycle.
Iron deficiencies
Iron deficiencies are frequently observed during flowering and can be challenging to distinguish from magnesium deficiencies.
The recommended approach is to enhance the use of products containing both nutrients since if one deficiency is present, the other is likely to follow or already be present.
Potassium deficiencies
Potassium deficiencies are also prevalent during the flowering phase. As potassium plays a vital role in bud enlargement. A lack of potassium becomes evident through yellowing and a burnt appearance on the edges of the leaf blades. Potassium-rich nutrients are readily available at gardening stores.
phosphorus deficiencies
While less common, phosphorus deficiencies can occur in cannabis plants during flowering. Symptoms include brown spotting or dark discoloration on older leaves, slowed growth, and the emergence of small new leaves.
To address this deficiency, it is advisable to remove the affected leaves. Also increase feeding with a phosphorus-rich nutrient product, which can be commonly found at gardening stores.
Check it out in our catalog
Infused Joints
Other Types of Cannabis Plant Deficiencies & A Word Of Caution

If you have mitigated issues regarding the previously mentioned types of nutrient deficiencies, you should be fine in your garden pursuits.
However, there are a handful of other deficiencies that can occur and that cultivators should be aware of:
- Zinc deficiencies — younger leaves start yellowing in between veins
- Calcium deficiencies — younger leaves curl
- Manganese deficiencies — yellowing leaves and brown spots, often confused with phosphorus deficiencies
- Copper deficiencies — leaves get dark and shiny
When it comes to cannabis nutrients, it’s important to remember that more is not always better. Not only are nutrients costly, but exceeding the necessary amount can be detrimental to the cannabis plant. In fact, overfeeding can lead to faster plant deterioration than underfeeding.
Novice cultivators often tend to overcompensate when they believe a plant lacks certain nutrients. One clear indication of nutrient overload is when the leaf tips appear burned. If this occurs, it is advisable to reduce nutrient usage and instead provide the plant with ample water.
Flushing the cannabis plants with 3-4 times the usual amount of water. Allow water to pass through the soil and drain from the containers is beneficial.
To assess the nutrient levels, test the water runoff after it has passed through the growing medium. If certain nutrients are excessively present in the runoff, refrain from feeding the cannabis plant those particular nutrients until the levels return to normal.
Even then, gradually reintroduce those nutrients at half the usual dosage for a few weeks following the flushing process.
Expert cultivators often recommend maintaining a garden journal to record feeding information and plant observations. This journal helps identify patterns and trends that may otherwise go unnoticed, including instances of overfeeding. Emphasizing education and the learning experience is crucial in this regard.
If you are interested not only in growing cannabis, but also in its use, then we recommend you
Purple Kraken [Indica] — Mini joint infused+kief
Strawberry Banana [Indica] — Mini joint infused+kief
In conclusion, understanding and addressing nutrient deficiencies in cannabis plants is essential for successful cultivation. By recognizing the common deficiencies during both the vegetative and flowering stages. For example, nitrogen and magnesium deficiencies, growers can take appropriate measures to provide the necessary nutrients.
Additionally, being aware of other deficiencies like iron, potassium and etc. allows cultivators to promptly identify and resolve any issues. It is crucial to remember that more nutrients do not always equate to better results.
By maintaining a balanced approach, utilizing proper flushing techniques, and keeping a garden journal to track observations, cultivators can optimize their cannabis cultivation experience and achieve healthier, more productive plants.
You can also read our article about cannabis plant “Male and female weed plants: What is the difference?”